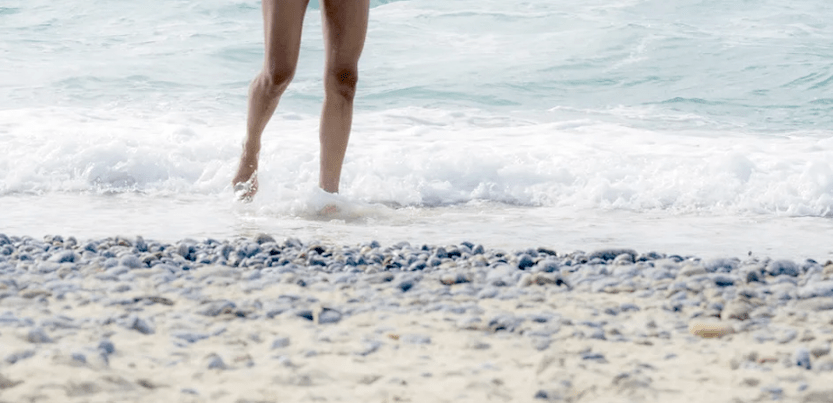
Varicose veins are an increase in the size of veins.Any superficial vein can become varicose, but the veins in the legs are most often affected.In an upright position (standing and walking), the pressure in the veins of the lower body increases.
For some, varicose veins and spider veins are simply a cosmetic problem, but for many people, varicose veins can cause heaviness and swelling in the lower extremities.Sometimes varicose veins lead to more serious problems - trophic ulcers.
Treatment may include both measures to prevent the development of chronic venous insufficiency and surgical procedures to remove veins (various techniques).
Symptoms of varicose veins
Varicose veins may not cause pain.Signs that indicate varicose veins include:
- Veins are dark purple or blue
- Veins that appear twisted and bulging;they are often like cords on your legs
When painful signs and symptoms occur, they may include:
- Feeling pain or heaviness in the legs
- Burning, throbbing, muscle spasms and swelling in the legs
- Itching around one or more veins
- Change in skin color around varicose veins
Spider veins are similar to varicose veins, but they are smaller.These veins are closer to the surface of the skin and are often red or blue.
Spider veins are found on the legs but can also be found on the face.They vary in size and often look like a spider's web.
When to see a doctor
If you have symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency and you want to determine the exact cause and completely get rid of the discomfort, then sign up for a consultation right now.Experienced phlebologists will check the condition of the vascular bed and give individual recommendations based on experience.
Causes of varicose veins
Weak or damaged valves can lead to varicose veins.Arteries carry blood from your heart to your tissues, and veins return blood to your heart.The veins in the legs work against gravity.
The contractions of the muscles in the lower legs act as a pump, and the walls of the elastic vein help blood return to your heart.Tiny valves in your veins open as blood flows toward your heart and then close to stop the blood flowing back.If these valves are weak or damaged, blood can flow backward and pool in the vein, causing the veins to stretch or twist.
Risk factors
These factors increase the risk of developing varicose veins:
- Age.The risk of varicose veins increases with age.Aging causes wear and tear on the vein valves that help regulate blood flow.Ultimately, wear and tear causes blood to flow back into your veins.
- Floor.Women are more likely to develop this disease.Hormonal changes during pregnancy, premenstruation, or menopause may be a factor because female hormones tend to reduce the elasticity of vein walls.Hormonal medications, such as birth control pills, may increase the risk of developing varicose veins.
- Pregnancy.During pregnancy, the volume of blood in your body increases.This change supports fetal growth, but can also lead to the unwanted side effect of dilated veins in the legs.Hormonal changes during pregnancy may also play a role.
- Family illness.If other family members have had varicose veins, you have a better chance.
- Obesity.Excess weight puts extra pressure on your veins.
- Standing or sedentary lifestyle.Your blood doesn't flow as well if you stay in the same position for a long time.
Complications
Complications of varicose veins, although rare, may include:
- Ulcer.Peptic ulcers can form on the skin near varicose veins, especially near the ankles.A discolored patch of skin usually appears before an ulcer forms.Call your doctor immediately if you suspect you have an ulcer.
- Blood clots.Sometimes the deep veins in the legs become enlarged.In such cases, the affected leg may become painful and swollen.Any persistent leg pain or swelling requires medical attention because it may indicate a blood clot, a condition medically known as thrombophlebitis.
- Bleeding.Sometimes veins very close to the skin can burst.This usually causes only minor bleeding.But any bleeding requires medical attention.
Prevention of varicose veins
There is no way to completely prevent varicose veins.But improving circulation and muscle tone can reduce the risk of developing varicose veins.Measures to treat discomfort from varicose veins at home:
- Gymnastics
- Maintaining an optimal body mass index
- High fiber, low salt diet
- Avoid high heels, tight hosiery and other tight clothing
- Leg Raising
- Change your sitting or standing position regularly
Well, it's time to move.